
Background
The Gramm Leach Bliley Act (GLBA) requires financial institutions to take steps to ensure the privacy, security and confidentiality of student records containing non-public customer information.
GLBA regulations include both a Privacy Rule (16 CFR 313) and a Safeguards Rule (16 CFR 314), both of which are enforced by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). The FTC considers the University to be a financial institution based on its student loan processing activities.
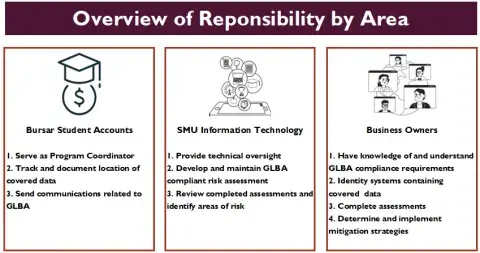
Bursar Student Accounts (BSA) works closely with SMU Information Security and business owners who maintain, store, transmit and process covered data to ensure compliance with all required components of GLBA.
This rule enforces several requirements related to the handling of non-public customer information.
The University is considered to be in compliance with the Privacy Rule through its adherence with the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act(FERPA). Information about FERPA is available on the University’s Registrar’s website: https://www.samuelmerritt.edu/registrars-office.
The Safeguards Rule applies to non-public customer information the University receives as well as other confidential financial information the University may choose to include within its scope.
Under the GLBA Safeguards Rule, the University is required to:
- Ensure the security and protection of customer information
- Protect against any anticipated threats or hazards to the security or integrity of such information
- Protect against unauthorized access to or use of such information that could result in substantial harm or inconvenience to any customer
Elements of the University’s GLBA program include the following:
Qualified Individual
The University has designated its Chief Information Officer (CIO) as the Qualified Individual to oversee its information security program. The CIO has overall responsibility for overseeing the University’s Information Security.
Risk Assessments
Risk assessments are the foundation upon which informed security management decisions are made.
The Information Security Policy establishes the requirement for all departments to participate in the Information Risk Management program.
The program requires the management of each department or unit to complete the process:
- at least annually
- when there are significant changes to departmental or unit IT resources, or
- when there are significant changes to the risk environment.
Business owners who maintain, operate, or manage information systems containing GLBA covered data are expected to conduct periodic risk assessments. In addition to performing risk assessments, business units are expected to implement mitigation strategies to reduce or eliminate identified risks.
A formal GLBA Safeguards Rule risk assessment will be conducted annually to identify where protected data resides, identify the responsible parties and to assess, identify, and document risks and to adjust the data protection plan as appropriate.
Data Protection
The University Information Security Policy policy states the codes of practice with which the University aligns its information security program.
The University’s Data Classification and Acceptable Use of University Data in the Cloud policy establishes a data protection strategy for all University information assets based upon sensitivity and defines responsibilities of members of the University community, each of whom has a duty to protect institutional data.
To guide users in maintaining the security, integrity, and privacy of confidential personal information and other data it collects or stores, the University has developed the University Data Protection Standards to highlight the requirements for handling and protecting data.
The standard is divided into many areas of protection:
- Confidentiality, Data & Security Policy
- Record Retention Policy
- Network Security (e.g., Servers, Network Attached Storage, Disk Arrays)
- Technology Acceptable Use Guidelines (e.g., Desktop Computers, Laptops, Tablets, Smart Phones, Mobile Devices)
In addition to the security requirements Department Managers and Chairs (e.g. direct reports to VPs and Deans; Directors) are required to follow the external data protection standards of GLBA.
Vulnerability Management
The Security of Connected Devices Standard outlines the vulnerability management requirements for devices that access, collect, generate, process, or transmit University data. Identified vulnerabilities must be addressed promptly, based on their risk severity. Annual penetration tests are conducted to assess information systems, and any discovered vulnerabilities are prioritized and incorporated into a remediation plan.
Training
GLBA requires the University to offer security awareness training to employees with access to covered data. These employees will be required to complete the “GLBA and Safeguarding Student Financial Information” training course in Workday on a regular basis. If training is not completed, access to covered data may be revoked.
Vendor Service Providers
The University Data Protection Standards include requirements for the review of third-party vendors that handle Highly Sensitive Data and/or mission critical services. The Vendor Security Review Standard requires business owners engaging third party vendors who process, store, or transmit High Sensitive Data to work with their vendor to complete a Required Risk Assessment. Information Security will review the risk assessment, assign a risk rating, and determine the steps needed to approve the procurement or continued use of the service.
Incident Response
The University’s Information Technology Incident Response Plan policy establishes a framework to prepare for, respond to, recover from, and mitigate against the effects of a wide range of disasters and emergencies that includes University-wide standards for emergency and continuity of operations planning (COOP) and Critical Incident Management Plan (CIMP). This policy applies to all University school/departments/units and its separate campuses. A coordinated and structured exercise program tests, validates, and identifies areas to sustain and for improvement in existing plans, procedures, and trainings. Per Code of Virginia Section 23.1-804 and Governor's Executive Order 41 (2019), at least one test or exercise of the CIMP and University COOP must be conducted annually.
The Information Security Policy establishes the requirement to report information security incidents to appropriate University officials so proper and timely response procedures can be initiated. Such reporting addresses particularly serious incidents, such as violations of confidentiality or integrity of sensitive University data. This standard applies to all users of University Information Technology (IT) resources.
Reporting
The Qualified Individual shall report in writing at least annually to the University’s Board of Visitors. The report must provide an overall assessment of the University’s compliance with this standard and cover specific topics related to the program, such as risk assessment, risk management and control decisions, service provider arrangements, security events and how management responded, and recommendations for changes to the covered data protection plan.
Records Management
The University’s Record Retention Policy and Matrix establishes agency requirements for the storage, retention, disposition and destruction of University electronic and physical records.
1. Question: How often will we have to complete a risk assessment?
Answer: GLBA requires the University to regularly assess risks in all systems that contain student financial information. As a result, you may be asked to conduct a risk assessment on an annual basis on all identified systems.
2. Question: How was the risk assessment designed?
Answer: The questions in the risk assessment were selected and customized using NIST SP 800-171 to meet the requirements of the GLBA Safeguards Rule. Specifically, the risk assessment aims to identify reasonably foreseeable internal and external risks to the security, confidentiality, and integrity of student financial information that could result in the unauthorized disclosure, misuse, alteration, destruction, or other compromise of such information.
3. Question: Why do we have to complete a risk assessment?
Answer: Risk assessments are required under 16 CFR Part 314.4(b)(2), Standards for Safeguarding Customer Information, which implements sections 501 and 505(b)(2) of GLBA.
4. Question: What should be included in a remediation plan.
Answer: Your remediation plan should be written and should describe how each identified risk will be mitigated and the timeline for remediating the risk.
5. Question: Will we be provided with a template or guidance on the remediation plan?
Answer: Development of the remediation plan will be the responsibility of the department or business unit that maintains or manages the system with the identified risks. You may need to work with your department or business unit’s leadership to prioritize and implement a mitigation strategy.
6. Question: What should we do if we have technical questions about implementing the remediation plan?
Answer: ITS Services can answer questions and assist you with the technology (e.g. networks and WiFi, storage, access) required to implement your remediation plan.
7. Question: What happens if we do not develop or implement a remediation plan?
Answer: Your remediation plan contributes to the University’s compliance with GLBA. If you do not develop and implement a remediation plan, your system may be disabled or disconnected from the network by IT.
In addition, if the University is not able to meet GLBA audit requirements, it may be subject to an audit finding. According to the Department of Education (ED), audit findings will be referred to the FTC and to Federal Student Aid’s Postsecondary Institution Cybersecurity Team (Cybersecurity Team). If the Cybersecurity Team determines that the University poses substantial risk to the security of student information, the University’s access to ED’s information systems may be temporarily or permanently disabled and the University will not be able to award or disburse federal student aid.
The terms listed here and their corresponding definitions apply to the GLBA compliance program.
Business Owner
Any University unit, department, area or employee who maintains, stores, transmits or processes covered data.
Covered Data
Non-public customer information required to be protected under GLBA. This also includes any data or information the University chooses to include even if not covered by GLBA. This information may be in paper, electronic, or other form.
Customer
Any person who is provided financial services by the University, such as obtaining a loan from the University or having a loan for which the University has servicing rights or responsibilities.
Financial Product or Service
Includes student loans, employee loans, activities related to extending credit, financial and investment advisory activities, management consulting and counseling activities, community development activities and other miscellaneous financial services (12 CFR 225.28).
Information System
Any location where covered data resides, including servers, networks, and computing stations.
Non-Public Customer Information
Any financial information or record given by a consumer to a financial institution for the purpose of obtaining a financial product. This information may be in paper, electronic, or other form. (16 CFR 313.3(n))
Nonpublic personal information means:
- Personally identifiable financial information.
- Any list, description, or other grouping of consumers (and publicly available information pertaining to them) that is derived using any personally identifiable financial information that is not publicly available.
Examples of nonpublic personal information include but are not limited to:
- Social Security Number
- Credit Card Number
- Account Numbers
- Account Balances
- Any Financial Transactions
- Tax Return Information
- Driver's License Number
- Date/Location of Birth
Examples of services or activities that the university may offer which result in the creation of customer information could include but are not limited to:
- Student (or other) loans, including receiving application information, and the making or servicing of such loans
- Credit counseling services
- Collection of delinquent loans and accounts
- Check cashing services
- Real estate settlement services
- Issuing credit cards or long term payment plans involving interest charges
- Obtaining information from a consumer report
Service Provider
Any person or entity that maintains, stores, transmits or processes customer information through its provision of services directly to the University.